
Spinal reflexes may cause the arms/legs to flex briskly in response to pain and must not be interpreted as a response.Ģ.2 Always record the best arm response. The following are important points to note when assessing a patient's level of consciousness using the Glasgow coma scale and calculating a Glasgow coma score (GCS).Ģ.1 The arms give a wider range of responses and for this reason are always observed using the Glasgow coma scale. Recommendations for assessing eye opening, verbal response and motor response are specified. The guidelines focus on the practical aspects of carrying out and interpreting the Glasgow coma scale and pupil responses. It is the method favoured by The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust and these guidelines have been developed to standardise practice so that the Glasgow coma scale and pupil responses can be assessed in a consistent manner to minimise misinterpretation.
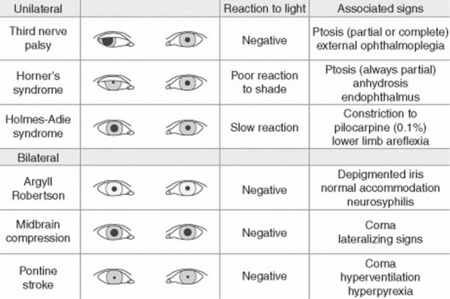
The Glasgow coma scale developed by Teasdale and Jennett (1974) is the most widely used assessment tool to measure a patient's level of consciousness. Introduction and BackgroundĪssessment of conscious level is an essential component of neurological examination and is usually performed together with assessment of pupillary size and reaction, vital signs, and focal neurological signs in the limbs. Guidelines for Assessing the Glasgow Coma Scale and Pupil Responses in Adultsĥ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
